Electric Flux
Electric Flux: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Electric Flux and Area Vector
Important Questions on Electric Flux
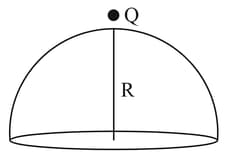
A point charge is placed just outside an imaginary hemispherical surface of radius as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
Given the electric field in the region is , find the net electric flux through the cube and the charge enclosed by it.
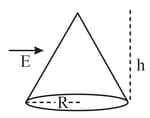
A uniform electric field is applied parallel to the base of a regular circular cone pyramid as shown. The flux through the curved surface is
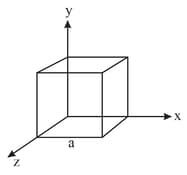
Coordinates of a square are given as , . If electric field is along z-axis, electric flux through square is
The image below shows two examples of electric field lines.
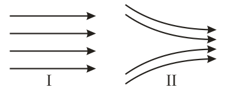
Which of the following statements is true?
A square sheet of is placed in an electric field such that the normal unit vector for the sheet is The electric flux through the sheet is:
An infinitely long line charge having linear charge density lies at a distance from center of an imaginary sphere of radius . Then
Consider a cube of side placed such that its six faces are given by equations and , placed in electric field given by . Find the electric flux crossing out of the cube in the unit of .
A cylinder of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by
Area vector is a vector quantity associated with each plane figure whose magnitude is
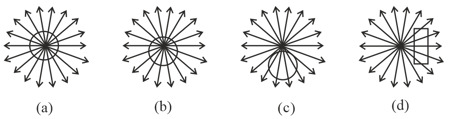
The black shapes in the figure below are closed surfaces. The electric field lines are in red. For which case, the net flux through the surfaces is non-zero?
A circular plate sheet of radius is placed in a uniform electric field of making an angle of with the field. Then find the electric flux through the sheet.
The net flux passing through the surface of an imaginary cube of edge length placed in space having a uniform volume charge density, is . The net flux passing through the surface of an imaginary sphere of radius in the same space is
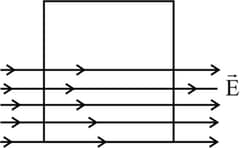
A square surface of side is in the plane of the paper. A uniform electric field also in the plane of the paper, is limited only to the lower half of the square surface, (see figure). The electric flux in SI units associated with the surface is:
Four equal charges are placed at centre of a conducting hollow sphere. If they are displaced from the centre, the change in flux will be (Radius of sphere ) :
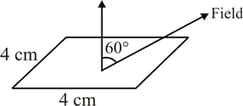
If a square coil is making an angle with electric field according to figure, the electric flux passing through the square coil is (the side of square is ):